Sponger ACL Rules
Introduction
The Virtuoso Sponger can be controlled via ACLs (Access Control Lists); basically, rules which define who is allowed to Sponge and who is not. It is also possible to restrict use of particular Sponger Cartridges. The ACL system is optional, and is enabled using a SPARQL pragma and the ACL Scope system as described below.
ACL Checking Layers
The Sponger can be accessed via several routes. These are depicted below. Sponging is provided as an optional service utilized by other service endpoints layered on top. For sponging to occur, the service layers above the Sponger, and also the graph security settings (both enforced by VAL and the RDF Graph Security System), must all grant sponge permission.
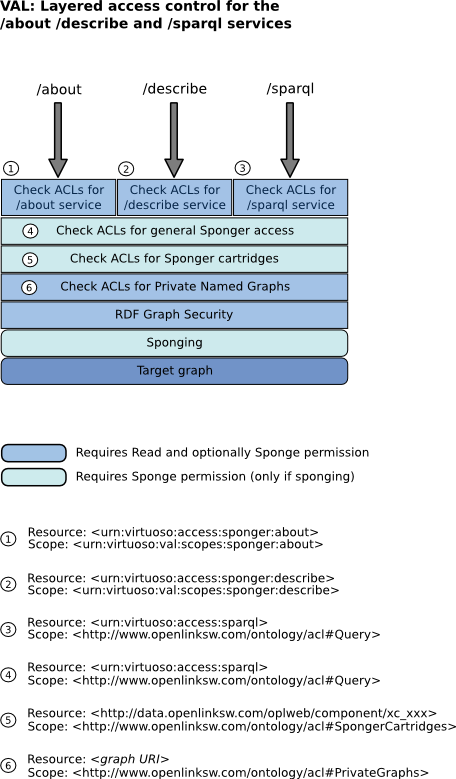
Having sponge permission means that sponging might occur (i.e. sponge attempts will not be blocked by VAL); it doesn't guarantee that sponging will occur. Whether sponging is done depends on whether the Sponger cache for the target data source URI is stale (as determined by the Sponger cache invalidation rules) and whether a re-sponge is forced through a Sponger option (the re-sponge option depends on which service is used to invoke sponging: /about, /describe or SPARQL).
Scopes Applicable to the Sponger
Two scopes control access to the Sponger:
- oplacl:Query
- Controls access to the Sponger in general and whether a user is able to sponge at all
- oplacl:SpongerCartridges
- Restricts access to particular Sponger cartridges
Enabling ACLs for General Sponger Use
By default, Sponger ACLs are disabled in all realms. (See also ACL Scopes in VAL.)
To enable evaluation of SPARQL ACL rules in the default realm (which includes services /sparql, /describe and /about, all of which support sponging) to determine whether the user may Sponge, enable the oplacl:Query scope.
This can be done through the Conductor UI or by executing the following SPARQL:
SPARQL
PREFIX oplacl: <http://www.openlinksw.com/ontology/acl#>
WITH <urn:virtuoso:val:config>
DELETE
{ oplacl:DefaultRealm oplacl:hasDisabledAclScope oplacl:Query }
INSERT
{ oplacl:DefaultRealm oplacl:hasEnabledAclScope oplacl:Query }
;
SPARQL ACLs refer to ACLs which regulate who has which SPARQL permissions (Read, Update, Sponge, List).
Enabling ACLs for Cartridge-Specific Control
By default, as with generic Sponger ACLs, Cartridge ACLs are disabled in all realms. (See also ACL Scopes in VAL.)
To enable evaluation of ACL rules in the default realm (which includes /sparql and /sponger, among others) for determination of whether the user may Sponge with a particular cartridge, execute the following SPARQL:
SPARQL
PREFIX oplacl: <http://www.openlinksw.com/ontology/acl#>
WITH <urn:virtuoso:val:config>
DELETE
{ oplacl:DefaultRealm oplacl:hasDisabledAclScope oplacl:SpongerCartridges }
INSERT
{ oplacl:DefaultRealm oplacl:hasEnabledAclScope oplacl:SpongerCartridges }
;
Next, enable cartridge ACLs using the Conductor UI. To do so, navigate to the Sponger's 'Configuration' panel under the 'Linked Data' > 'Sponger' tabs, then select 'ABAC' as the cartridge ACL mode.
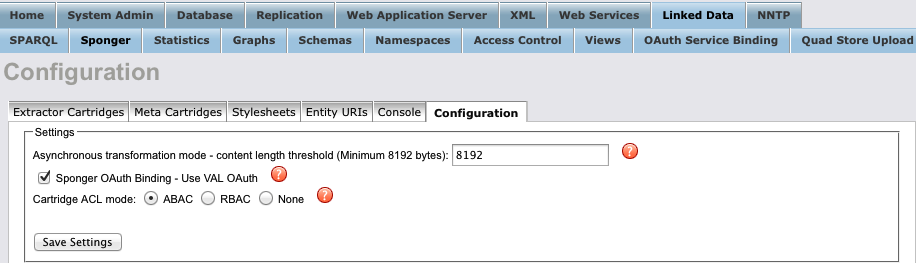
- Virtuoso supports two types of cartridge ACLs for protecting access to Sponger cartridges - ABAC and RBAC ACLs. ABAC cartridge ACLs are VAL-based, and configured and managed through VAL. RBAC cartridge ACLs are SQL-role-based, and are configured and managed through the Conductor UI's 'Access Control List' panel accessible from the 'Linked Data' > 'Access Control' tab.
- In the Configuration panel, option 'ABAC' is disabled if the VAL VAD isn't installed. 'None' results in no cartridge ACLs of either type being applied. If option 'ABAC' is selected, scope oplacl:SpongerCartridges must be enabled for VAL cartridge ACLs to take effect.
- When the Cartridges VAD is first installed, the cartridge ACL mode is initialized to 'ABAC' if the VAL VAD is present, or 'None' otherwise. Once initialized, any cartridge ACL mode subsequently set through the Conductor UI remains in effect. If the VAL VAD is uninstalled and the cartridge ACL mode is 'ABAC', the mode is reset to 'None'.
Usage
Before using the ACL engine, it is important to load the Openlink ACL Ontology into the VAL ACL Schema graph:
SPARQL
LOAD <http://www.openlinksw.com/ontology/acl#>
INTO <urn:virtuoso:val:acl:schema>
;
For Sponger ACL rules to be enforced by the SPARQL engine, the "get:enforce-acls" pragma must be set.
When VAL is installed, /sparql will do this automatically:
SPARQL
DEFINE get:enforce-acls "yes"
SELECT ....
The Rules can be controlled via the RESTful VAL ACL API or the Internal VAL API. Alternatively, one can explicitly add the rules to the private graph matching the realm in which the rules should apply. Given the default realm --
http://www.openlinksw.com/ontology/acl#DefaultRealm
-- and default hostname "HOST" the graph IRI would be --
http://HOST/acl/graph/rules/http%3A%2F%2Fwww.openlinksw.com%2Fontology%2Facl%23DefaultRealm
-- and the groups will be stored in named graph --
http://HOST/acl/graph/groups/http%3A%2F%2Fwww.openlinksw.com%2Fontology%2Facl%23DefaultRealm
Be aware that these graphs can be customized for better readability.
ACL Resources
Generic Sponger ACL Resource
To grant the right to Sponge in general, there is only one resource of importance: urn:virtuoso:access:sparql.
Whoever has oplacl:Sponge permissions on this virtual resource can sponge in the given realm.
(See SPARQL and named graph ACLs for details).
Sponger Cartridge ACLs
Each Cartridge is described as an RDF resource, and has a URI uniquely identifying it.
These URIs must be used in ACL rules governing the use of that specific cartridge.
As with generic Sponger access, the access mode is oplacl:Sponge.
To date, Sponger cartridge URIs are built from a common prefix, http://data.openlinksw.com/oplweb/component/xc_, plus the lowercase internal name of the cartridge.
For example, the Wine cartridge has URI http://data.openlinksw.com/oplweb/component/xc_wine.
Graph <urn:virtuoso:sponger:cartridges> contains the full list of cartridge URIs.
There is one special URI, which denotes all installed cartridges in a given Virtuoso instance: http://data.openlinksw.com/oplweb/component/xc_all.
Be aware that the ACL graphs can be customized for better readability.
Sponger ACL Rule Examples
In the following examples --
- The default realm oplacl:DefaultRealm is used for creating the ACL resources.
- "HOST" is used as a placeholder for the default hostname of the system the ACL resource are created on.
Generic Sponging ACL Examples
See SPARQL and named graph ACLs for more examples.
Allow everyone to sponge
SPARQL
PREFIX acl: <http://www.w3.org/ns/auth/acl#>
PREFIX oplacl: <http://www.openlinksw.com/ontology/acl#>
PREFIX foaf: <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/>
WITH <http://HOST/acl/graph/rules/http%3A%2F%2Fwww.openlinksw.com%2Fontology%2Facl%23DefaultRealm>
INSERT
{
<#a1> a acl:Authorization ;
foaf:maker <http://HOST/dataspace/person/dba#this> ;
oplacl:hasAccessMode oplacl:Sponge ;
acl:accessTo <urn:virtuoso:access:sparql> ;
acl:agentClass foaf:Agent ;
oplacl:hasScope oplacl:Query ;
oplacl:hasRealm oplacl:DefaultRealm
};
Allow user "demo" to grant Sponging permissions
By default, only "dba" and administrators can grant sponging permissions. When this rule in in place, user "demo" can create additional ACL rules granting sponging permissions to others.
SPARQL
PREFIX acl: <http://www.w3.org/ns/auth/acl#>
PREFIX oplacl: <http://www.openlinksw.com/ontology/acl#>
PREFIX foaf: <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/>
WITH <http://HOST/acl/graph/rules/http%3A%2F%2Fwww.openlinksw.com%2Fontology%2Facl%23DefaultRealm>
INSERT
{
<#a1> a acl:Authorization ;
foaf:maker <{ADMIN-IRI}> ;
oplacl:hasAccessMode oplacl:GrantSponge ;
acl:accessTo <urn:virtuoso:access:sparql> ;
acl:agent <http://HOST/dataspace/person/demo#this> ;
oplacl:hasScope oplacl:Query ;
oplacl:hasRealm oplacl:DefaultRealm .
};
Grant Sponge Permissions to a Group Of People
There are two types of groups:
- static -- a simple list of individuals
- conditional -- a set of conditions which define a dynamic group of individuals
The rule to grant Sponge permissions to a group looks exactly like the one for granting permissions to an individual:
SPARQL
PREFIX acl: <http://www.w3.org/ns/auth/acl#>
PREFIX oplacl: <http://www.openlinksw.com/ontology/acl#>
PREFIX foaf: <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/>
WITH <http://HOST/acl/graph/rules/http%3A%2F%2Fwww.openlinksw.com%2Fontology%2Facl%23DefaultRealm>
INSERT
{
<#a1> a acl:Authorization ;
foaf:maker <{ADMIN-IRI}> ;
oplacl:hasAccessMode oplacl:Sponge ;
acl:accessTo <urn:virtuoso:access:sparql> ;
acl:agent <#group> ;
oplacl:hasScope oplacl:Query ;
oplacl:hasRealm oplacl:DefaultRealm .
};
Grant Sponge Permissions to a Static Group
SPARQL
PREFIX oplacl: <http://www.openlinksw.com/ontology/acl#>
PREFIX foaf: <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/>
WITH <http://HOST/acl/graph/groups/http%3A%2F%2Fwww.openlinksw.com%2Fontology%2Facl%23DefaultRealm>
INSERT
{
<#group> a foaf:Group,
oplacl:StaticGroup ;
foaf:name "Some people" ;
foaf:member <http://dduck.wordpress.com> ,
<http://peterparker.tumblr.com/> .
};
Grant Sponge Permissions to Anyone Who Is Authenticated
The Required Group in a conditional group which includes every authenticated NetID?:
SPARQL
PREFIX oplacl: <http://www.openlinksw.com/ontology/acl#>
PREFIX foaf: <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/>
WITH <http://HOST/acl/graph/groups/http%3A%2F%2Fwww.openlinksw.com%2Fontology%2Facl%23DefaultRealm>
INSERT
{
<#group> a foaf:Group ,
oplacl:ConditionalGroup ;
foaf:name "Valid Identifiers" ;
oplacl:hasCondition [
a oplacl:GroupCondition ,
oplacl:GenericCondition ;
oplacl:hasCriteria oplacl:NetID ;
oplacl:hasComparator oplacl:IsNotNull ;
oplacl:hasValue 1
]
};
Grant Sponge Permissions to any Verified WebID
The Required Group in a conditional group which includes every authenticated NetID?:
SPARQL
PREFIX oplacl: <http://www.openlinksw.com/ontology/acl#>
PREFIX foaf: <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/>
WITH <http://HOST/acl/graph/groups/http%3A%2F%2Fwww.openlinksw.com%2Fontology%2Facl%23DefaultRealm>
INSERT
{
<#group> a foaf:Group ,
oplacl:ConditionalGroup ;
foaf:name "Valid WebIDs" ;
oplacl:hasCondition [
a oplacl:GroupCondition,
oplacl:GenericCondition ;
oplacl:hasCriteria oplacl:WebIDVerified ;
oplacl:hasComparator oplacl:EqualTo ;
oplacl:hasValue 1
]
};
Grant Sponge Permissions to any Valid X.509 Client Certificate
The Required Group in a conditional group which includes every valid X.509 certificate:
SPARQL
PREFIX oplacl: <http://www.openlinksw.com/ontology/acl#>
PREFIX foaf: <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/>
WITH <http://HOST/acl/graph/groups/http%3A%2F%2Fwww.openlinksw.com%2Fontology%2Facl%23DefaultRealm>
INSERT
{
<#group> a foaf:Group,
oplacl:ConditionalGroup ;
foaf:name "Valid X.509 Certificates" ;
oplacl:hasCondition [
a oplacl:GroupCondition,
oplacl:GenericCondition ;
oplacl:hasCriteria oplacl:CertVerified ;
oplacl:hasComparator oplacl:EqualTo ;
oplacl:hasValue 1
]
};
Grant Sponge Permissions to any Verified WebID Which Claims to be a Person
Query conditions consist of a query which supports two variables which are replaced with the profile graph and the personal URI respectively.
SPARQL
PREFIX oplacl: <http://www.openlinksw.com/ontology/acl#>
PREFIX foaf: <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/>
WITH <http://HOST/acl/graph/groups/http%3A%2F%2Fwww.openlinksw.com%2Fontology%2Facl%23DefaultRealm>
INSERT
{
<#group> a foaf:Group, oplacl:ConditionalGroup ;
foaf:name "Valid WebIDs" ;
oplacl:hasCondition [
a oplacl:GroupCondition,
oplacl:GenericCondition ;
oplacl:hasCriteria oplacl:WebIDVerified ;
oplacl:hasComparator oplacl:EqualTo ;
oplacl:hasValue 1
] ,
[
a oplacl:GroupCondition,
oplacl:QueryCondition ;
oplacl:hasQuery """ASK WHERE { GRAPH ^{graph}^ { ^{uri}^ a foaf:Person } }"""
]
};
Cartridge-Specific ACL Examples
Grant the Right to Use a Specific Cartridge to Everyone
Everyone is allowed to Sponge using the Facebook Graph Cartridge:
SPARQL
PREFIX acl: <http://www.w3.org/ns/auth/acl#>
PREFIX oplacl: <http://www.openlinksw.com/ontology/acl#>
PREFIX foaf: <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/>
WITH <http://HOST/acl/graph/rules/http%3A%2F%2Fwww.openlinksw.com%2Fontology%2Facl%23DefaultRealm>
INSERT
{
<#a1> a acl:Authorization ;
foaf:maker <{ADMIN-IRI}> ;
oplacl:hasAccessMode oplacl:Sponge ;
acl:accessTo <http://data.openlinksw.com/oplweb/component/xc_facebook_opengraph> ;
acl:agentClass foaf:Agent ;
oplacl:hasScope oplacl:SpongerCartridges ;
oplacl:hasRealm oplacl:DefaultRealm
};