Creating a Windows Forms Application To Access RDF Data Using The Virtuoso ADO.Net Provider
- Introduction
- Prerequisites
- Creating the Application
- Step 1 - Create a view of the RDF data
- Step 2 - Create a simple grid form in Visual Studio
- Step 3 - Change the mapping of the DataSet
- Step 4 - Create the on_click event handler for the cells in the DataGridView
- Step 5 - Create a class to handle exploring the RDF data
- Step 6 - Add a new Data Set to hold the query results
- Step 7 - Build and run the application
- Next Steps
Introduction
This document will guide you through creating a simple application that allows you to access RDF data in a Virtuoso database as an Entity DataSet and explore that RDF data in an intuitive way by clicking on dereferenceable IRIs.
Prerequisites
- Microsoft Visual Studio 2008
- The Virtuoso ADO.Net provider for .Net 3.5 and the Entity Framework
- The example assumes that you have a local Virtuoso server with the Northwind demo database installed.
If the demo database is not already installed then download the demo database VAD package (
demo_dav.vad) and install it. The VAD package will create a new database in Virtuoso called demo containing the familiar Northwind tables. It will also creates Linked Data Views of the Northwind tables. In the example we assume the database is accessible on a hostname of "demo.openlinksw.com" on the default port80, where an actually live instance of the Virtuoso Demo database is hosted. Users would use the appropriate hostname and port number of their Virtuoso installation to create the sample application, and would belocalhost:8890for a default installation or whatever theURIQA DefaultHostVirtuoso configuration parameter is set to when the demo database VAD package is installed.
Creating the Application
Step 1 - Create a view of the RDF data
We want to be able to access the RDF data in Visual Studio and the easiest way to do this is to create a view of the data that we are interested in and bind that view to a DataSet. This can be considered as using server side SPARQL. Virtuoso supports an extension to standard SQL that allows execution of SPARQL within a SQL statement. If a SQL query begins with the keyword SPARQL then the rest of the query is interpreted by as SPARQL. If a SPARQL query is used as the definition of a view then that view can be manipulated using SQL like any other view. In this way the result set from a SPARQL query can be easily accessed from Visual Studio using ADO.Net and the Entity Framework.
- To create a view of the customers in the Northwind, first open the Virtuoso Conductor and log in as dba.
-
Note:
- If the view is added to the Visual Studio project as user "demo" (or any other than "dba'), then it must be ensured that the "SPARQL_SELECT" and "SPARQL_SPONGE" roles are assigned to this user, which can be done via the Virtuoso Conductor in the "System Admin" -> "User Accounts" tab.
- Execute permissions will also need to be granted to the following procedure:
GRANT EXECUTE ON DB.DBA.RDF_MAKE_LONG_OF_SQLVAL TO "demo"
-
Note:
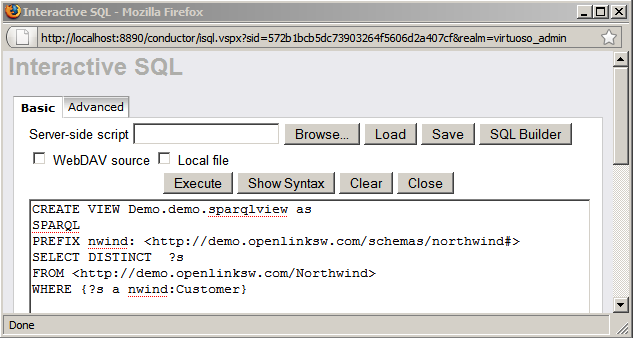
- Then open iSQL from the menu on the left and execute the following statement --
CREATE VIEW Demo.demo.sparqlview AS SPARQL PREFIX nwind: <http://demo.openlinksw.com/schemas/northwind#> SELECT DISTINCT ?s FROM <http://demo.openlinksw.com/Northwind> WHERE { ?s a nwind:Customer }
Step 2 - Create a simple grid form in Visual Studio
- Open Visual Studio and create a new Windows Forms Application called RDFDemo.
- In the Form Designer drag a DataGridView on to the form.
- Click the Choose Data Source drop down and select Add Project Data Source.
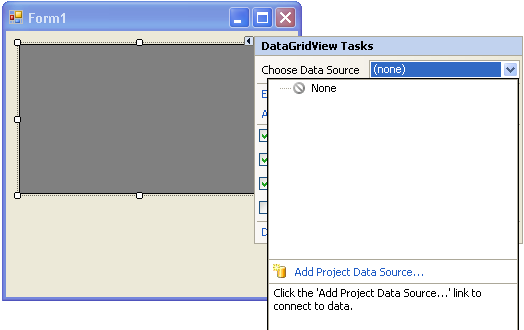
- In the Data Source Configuration Wizard choose Database and then set up a connection to the demo database on your local Virtuoso server.
- On the Choose Your Data Objects page expand the Views and select sparqlview.
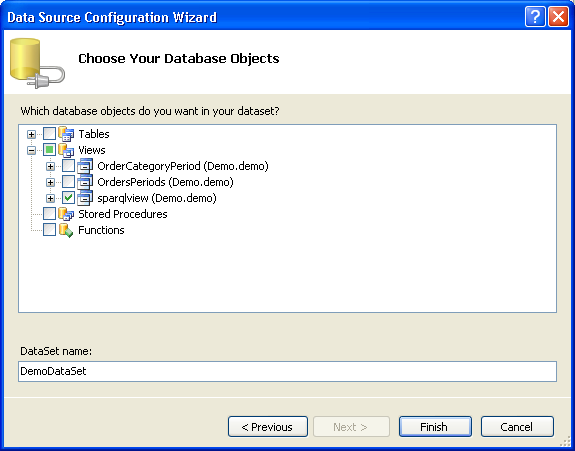
- Click Finish.
- In the Form Designer select dataGridView1 and change the AutoSizeColumnsMode to AllCellsExceptHeader.
- Select the DefaultCellStyle and click on the ellipsis.
This will open the CellStyleBuilder.
Change the ForeColor to Blue.
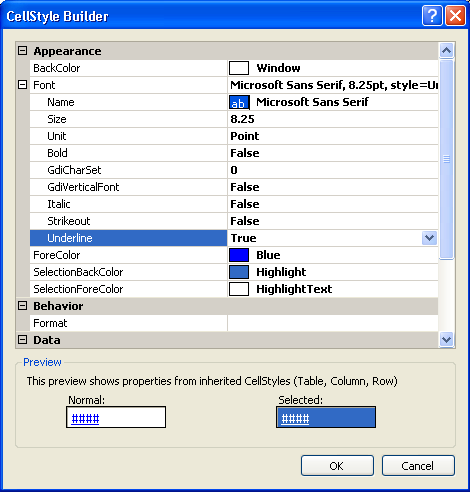
- Expand Font and change Underline to True. Click OK.
Step 3 - Change the mapping of the DataSet
- In the Solution Explorer you will now have a DataSet called DemoDataSet.xsd.
- If you double click on this it opens the DataSet Designer.
- Select the column called s in the sparqlview table, and in the Properties pane, change the DataType from System.String to System.Object.
- The data returned by a SPARQL query can either be an IRI or a literal value. In order to distinguish between the two the Virtuoso ADO.Net provider defines an additional data type, SQLExtendedString. By setting the column type to System.Object we can cast the fetched data back to SQLExtendedString and find out if an individual value is an IRI or a literal and handle it appropriately.
Step 4 - Create the on_click event handler for the cells in the DataGridView
- Return to the Form Designer and double click on the cell of the DataGridView. This creates the dataGridView1_CellContentClick method in Form1.cs. This is the method that handles clicking on IRI objects in the grid.
- Paste the following block of code into the body of the dataGridView1_CellContentClick method.
int column = e.ColumnIndex; object o = dataGridView1.Rows[e.RowIndex].Cells[e.ColumnIndex].Value; Type t = dataGridView1.Rows[e.RowIndex].Cells[e.ColumnIndex].ValueType; if (o is SqlExtendedString) { SqlExtendedString se = (SqlExtendedString) o; ExtendedStringHandler seHandler = new ExtendedStringHandler(se, this.sparqlviewTableAdapter.Connection); seHandler.displayData(); } else if (o is SqlRdfBox) { //doesn't do anything at the moment }
- As we are using the SQLExtendedString extension from the Virtuoso ADO.Net provider you will also need to add
using OpenLink.Data.Virtuoso;
at the top of the file.
Step 5 - Create a class to handle exploring the RDF data
- Add a new C# class to the project called ExtendedStringHandler, by right-clicking on RDFDemo in the Solution Explorer and Add a Class.
- Add the following using statements to the top of the file
using OpenLink.Data.Virtuoso; using System.Data; using System.Windows.Forms; using System.Drawing; using System.Data.Mapping; using System.Data.Common;
- Paste the following block of code into the class definition.
StringBuilder DescribeCommand; VirtuosoConnection ParentConnection; List<Label> labelList = new List<Label>(); List<TextBox> textBoxList = new List<TextBox>(); DescribeDataSet describeDataSet = new DescribeDataSet(); Boolean isIRI = false; public ExtendedStringHandler(SqlExtendedString iri, VirtuosoConnection parentConnetion) { ParentConnection = parentConnetion; if (iri.IriType == SqlExtendedStringType.IRI) { isIRI = true; DescribeCommand = new StringBuilder("sparql SELECT * FROM <http://demo.openlinksw.com/Northwind> WHERE {<" + iri.ToString() + "> ?p ?o}"); // Replace demo.openlinksw.com in line above with your URIQA DefaultHost setting } } public string describeCommandText { get { return DescribeCommand.ToString(); } } public void getDescribeData() { VirtuosoCommand myCommand = new VirtuosoCommand(this.describeCommandText, this.ParentConnection); VirtuosoDataAdapter myAdapter = new VirtuosoDataAdapter(); myAdapter.SelectCommand = myCommand; myAdapter.Fill(describeDataSet.DataTable1); } public void displayData() { if (isIRI) { getDescribeData(); Form describeForm = new Form(); describeForm.AutoScroll = true; describeForm.Width = 840; Label label1 = new Label(); label1.AutoSize = true; label1.Font = new Font(label1.Font.FontFamily, label1.Font.Size + 3.0F, label1.Font.Style | FontStyle.Bold, label1.Font.Unit); describeForm.Controls.Add(label1); DataTable table1 = describeDataSet.Tables[0]; if (table1.Rows.Count == 0) label1.Text = "No Details Available"; else { foreach (DataRow row in table1.Rows) if (row[0].ToString() == "http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#type") { StringBuilder title = new StringBuilder(row[1].ToString() + " details"); label1.Text = title.ToString(); break; } foreach (DataRow row in table1.Rows) { Label propertyLabel = new Label(); TextBox valueBox = new TextBox(); valueBox.Width = 400; object property = row[0]; object value = row[1]; if (value is SqlExtendedString) { valueBox.ForeColor = Color.Blue; valueBox.Font = new Font(valueBox.Font.FontFamily, valueBox.Font.Size, valueBox.Font.Style | FontStyle.Underline, valueBox.Font.Unit); } propertyLabel.Text = row[0].ToString(); propertyLabel.AutoEllipsis = true; propertyLabel.AutoSize = false; propertyLabel.Width = propertyLabel.PreferredWidth > 380 ? 380 : propertyLabel.PreferredWidth; Binding bind = new Binding("Text", row[1], ""); valueBox.DataBindings.Add(bind); labelList.Add(propertyLabel); textBoxList.Add(valueBox); } for (int i = 0; i < table1.Rows.Count; i++) { textBoxList[i].Click += new EventHandler(this.iri_Click); labelList[i].Location = new Point(10, i * 20 + 50); textBoxList[i].Location = new Point(400, i * 20 + 50); describeForm.Controls.Add(labelList[i]); describeForm.Controls.Add(textBoxList[i]); } describeForm.Height = labelList.Count * 20 + 100 > 500 ? 500 : labelList.Count * 20 + 100; } describeForm.ShowDialog(); } else { Form blankForm = new Form(); Label label1 = new Label(); label1.Text = "Blank Node"; label1.Font = new Font(label1.Font.FontFamily, label1.Font.Size + 3.0F, label1.Font.Style | FontStyle.Bold, label1.Font.Unit); blankForm.ShowDialog(); } } public void iri_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { int boxNum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < textBoxList.Count; i++) { if (sender == textBoxList[i]) { boxNum = i; break; } } Object o = describeDataSet.DataTable1.Rows[boxNum][1]; if (o is SqlExtendedString) { SqlExtendedString se = (SqlExtendedString)o; ExtendedStringHandler seHandler = new ExtendedStringHandler(se, ParentConnection); seHandler.displayData(); } else if (o is SqlRdfBox) { //doesn't do anything at the moment } }
- The ExtendedStringHandler class creates a new SPARQL query based on the IRI that was clicked. This query is executed against Virtuoso using the ADO.Net connection in the same way that any SQL statement would be executed across an ADO.Net connection. This can be considered as Client Side SPARQL. The result set from the query describes the selected object and is returned as an ADO.Net DataAdapter. The DataAdapter is used to fill a DataTable which is displayed on a new form. We now need to add the new DataSet to the project and define the DataTable that will hold the query results.
Step 6 - Add a new Data Set to hold the query results
- Right click RDFDemo in the Solution Explorer and add a new DataSet.
Call the new DataSet DescribeDataSet.
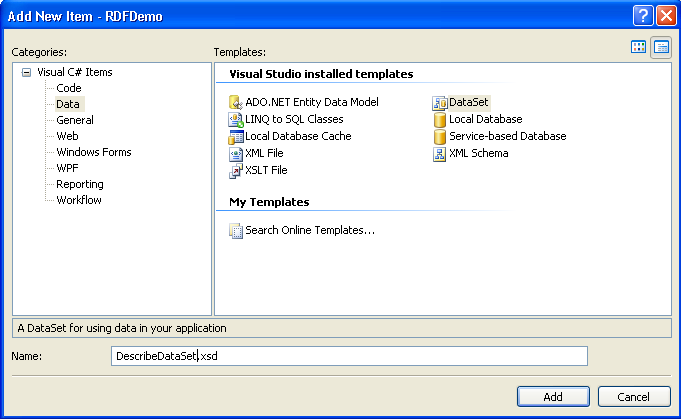
- Double click on DescribeDataSet in the Solution Explorer to open the DataSet Designer and drag a DataTable from the Toolbox into it.
- Add two columns, p and o, to the DataTable and set the DataType of each column to System.Object.
Step 7 - Build and run the application
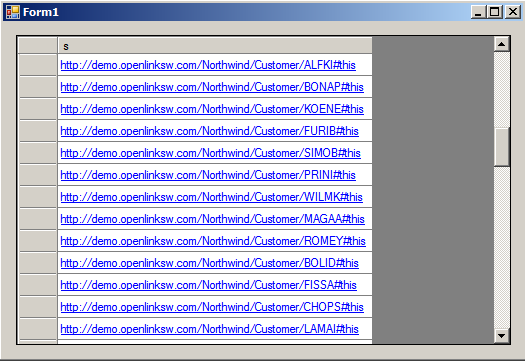
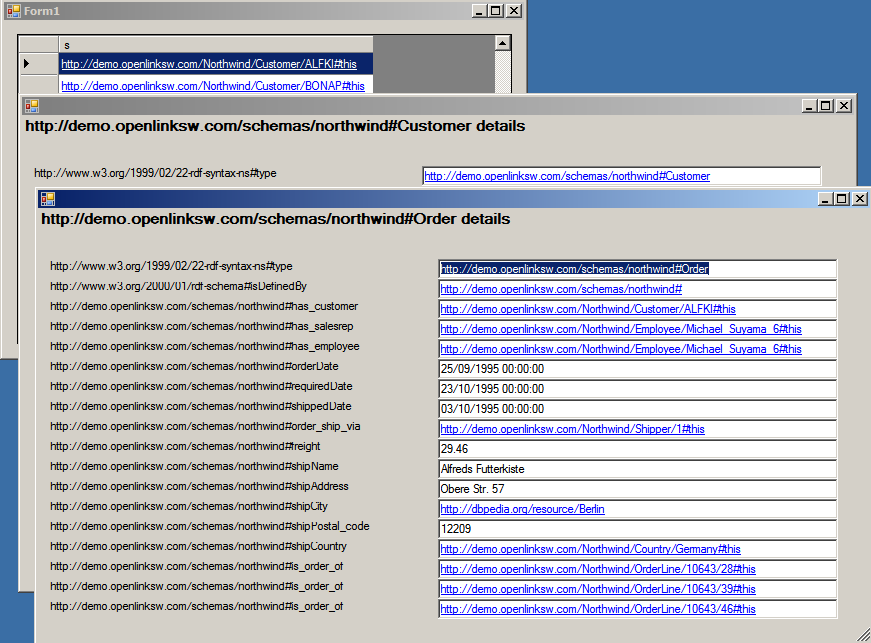
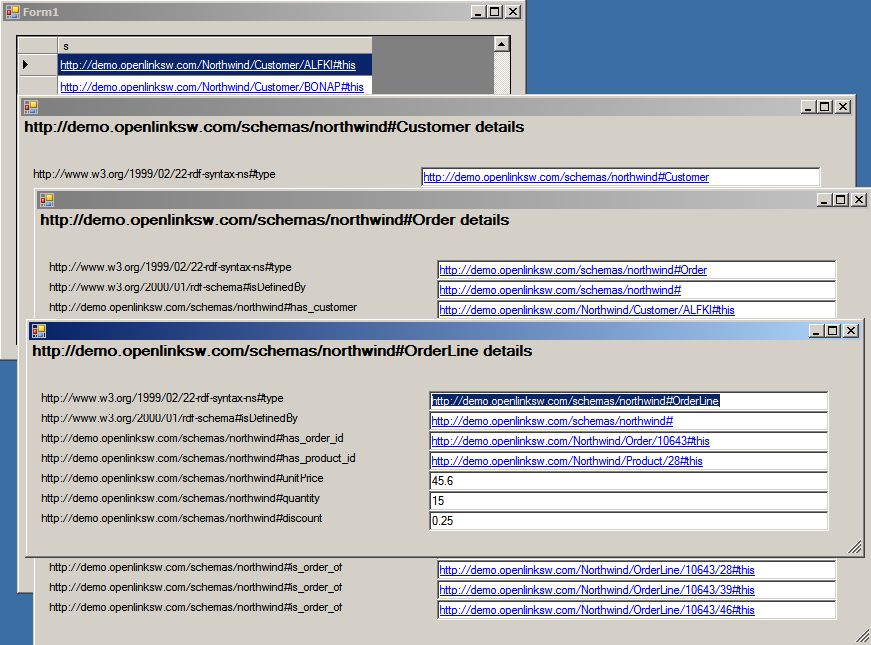
- You should see a form displaying all the Northwind customers, like this.
- When any customer is clicked it opens a new form showing customer details.
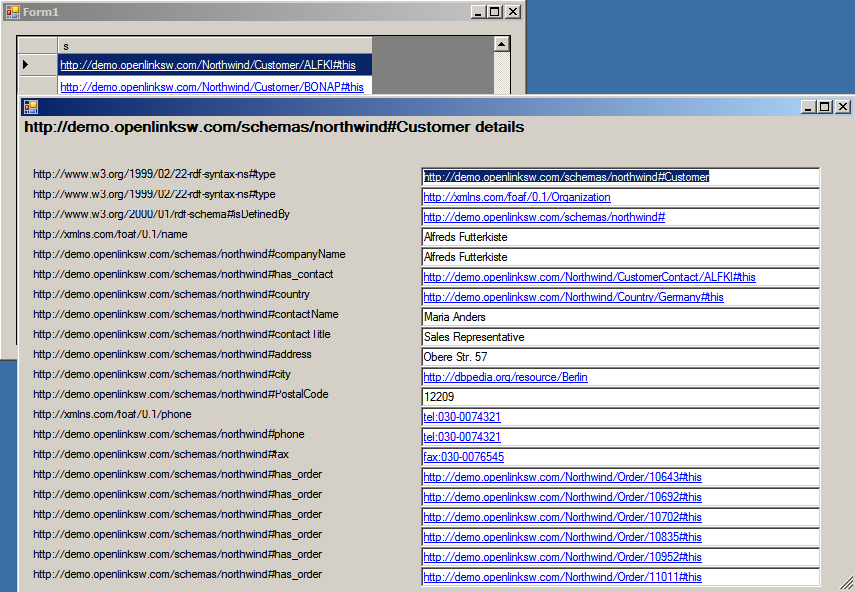
- Clicking on the links in the new form allows you to drill down further to get order, product, location details etc.
Next Steps
You will notice if you keep clicking on the links that this application will only display data that is held in the Northwind graph. Clicking on an external link, for example the link to Berlin in dbpedia, http://dbpedia.org/resource/Berlin, results in a empty window and an error message. The next step is to extend this application so that it can handle dereferencing external IRIs.